Diabetes mellitus is accompanied by the inability to absorb glucose with its subsequent accumulation in the blood. Type 2 disease manifests itself in a milder form than type 1. The basis of treatment for the disease is diet and medications.
Type 2 diabetes: characteristics of the disease
For normal functioning, the body needs a constant supply of energy, which is produced from the food consumed. The main supplier is glucose. To absorb sugar into the tissues, a hormone is needed - insulin, produced by the pancreas.
In type 2 diabetes, the gland functions normally, but the cells develop resistance to the hormone. As a result, sugar is not delivered to the cells, but remains in the blood plasma. The body begins to lack energy. The brain reacts to the situation with a signal to increase insulin production.Increasing the concentration of the hormone does not change the situation.
Gradually, insulin production decreases significantly, due to organ wear and depletion of reserves, and may stop completely. The disease develops gradually and initially has no pronounced symptoms. With an advanced form of the disease, it can progress to stage 1.
Reasons for development
Type 2 diabetes often develops due to wear and tear on the body, so the pathology is more common in people over 40 years of age.
But there are other reasons and provoking factors for the development of the disease:
- transmission at the genetic level. If you have relatives suffering from diabetes (of any type), the probability of developing the disease increases by 50%;
- obese people are more predisposed to developing the disease, since fat deposits reduce the sensitivity of cells and also reduce the functioning of organs;
- incorrectly composed diet. Frequent consumption of sweet, fatty and quickly digestible foods;
- low consumption of energy reserves, occurs with a small amount of physical activity;
- pathological changes in the pancreas;
- frequent infectious diseases that affect the functioning of the digestive tract;
- nervous and physical exhaustion, as well as frequent stress and depression;
- frequent increase in blood pressure;
- violation of taking medications with the development of side effects that affect the functioning of the gland.
The pathology develops when there are 2 or 3 causes at the same time. Sometimes the disease is diagnosed in pregnant women. In this case, its appearance is associated with hormonal changes in the body. The disease (usually) goes away on its own after giving birth.
What happens with diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (diet and drug treatment are interconnected: without following a diet, taking medications will be ineffective) affects the functioning of the entire organism. As the disease begins to develop, tissue sensitivity to insulin decreases. The pancreas and other organs function normally.
Without adequate treatment, the concentration of glucose in the blood increases, which leads to the "sugaring" of protein cells in the blood. This change disrupts the functioning of the organs. The body experiences a shortage of energy, which also leads to a malfunction of all systems.
The lack of energy begins to be replenished by the breakdown of fat cells. The process is accompanied by the release of toxins that poison the entire body and affect the performance of brain cells.
Excess sugar leads to dehydration; beneficial vitamins and minerals are flushed out with water. The condition of the blood vessels worsens, which leads to rupture of the heart. It also increases the risk of blockage of blood vessels due to blood clots. As a result, vision, liver and kidney function are impaired, as these organs contain many small blood vessels. Blood circulation in the extremities is compromised.
Symptoms of type 2 diabetes
In the initial stage, the disease occurs without visible symptoms. If the disease is not detected or adequate treatment is not received, the pathology develops furtheraccompanied by characteristic symptoms:
- a constant sensation of dryness in the mouth, accompanied by an unquenchable thirst. This symptom occurs because a large amount of fluid is needed to remove excess glucose from the blood. The body spends on this all the fluid and water incoming from the tissues;
- the formation of a large amount of urine, as a result of which the person often goes to the toilet;
- increased sweating, which increases during sleep;
- increased dryness of the skin and mucous membranes, accompanied by itching;
- lack of humidity and poor nutrition of the optic nerve cause vision problems;
- microcracks and wounds heal more slowly;
- arbitrary contraction of muscle tissue occurs due to a malfunction of the nervous system;
- swelling of the limbs accompanied by pain and numbness;
- due to lack of energy, severe weakness, increased appetite and arrhythmia are felt;
- a sharp decrease in immunity, which causes frequent colds.
In the initial phase, an increase in appetite, fatigue and a frequent need for fluids are observed. To exclude/confirm diabetes you need to contact your family doctor/paediatrician for a blood sugar test. At the beginning of the disease it is enough to adapt the diet for treatment.
Phases
Depending on the severity of symptoms, features of treatment and complications arising from the disease, diabetes is divided into 4 degrees of severity.
| Degrees of pathology | Main features | Distinguishing features |
|---|---|---|
| Light | The disease is manifested by a slight increase in blood sugar concentration, which causes increased thirst, increased appetite and muscle weakness. There are no pathological changes in the functioning of the body. Nutritional adjustments are used as therapy. In rare cases, medicines are prescribed. | At this stage, diabetes is detected in rare cases, mainly during medical examinations during blood testing. The composition of urine does not change. Glucose levels are between 6 and 7 mmol/l. |
| Average | The symptoms of the disease increase. There is a deterioration in the functioning of the organs of vision and blood vessels, and the blood supply to the extremities is interrupted. There are no serious abnormalities in the functioning of the body. Treatment includes diet and medications. | The sugar level in the urine is normal, in the blood the range is 7-10 mmol/l. |
| Heavy | The symptoms are pronounced. There is a serious malfunction in the functioning of organs (decreased vision, constantly high blood pressure, pain and tremors in the extremities). Treatment uses a strict menu and insulin administration (drug therapy does not produce results). | Increased sugar levels are recorded in urine and blood. In the blood, the concentration varies in the range 11-14 mmol/l. |
| Greater gravity | The impairment of organ functioning is practically irreversible. The disease cannot be cured, constant monitoring of sugar and its regulation with insulin injections is necessary. | The glucose concentration remains in the range 15-25 mmol/l. A person often falls into a diabetic coma. |
Mild to moderate diabetes is easy to treat and control blood sugar. In these stages, there is no significant disruption in the functioning of the body. Diet, weight loss, and medications can sometimes allow for a full recovery.
Diagnostics
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (diet and treatment are prescribed after diagnosis) is determined by laboratory methods. Additionally, a hardware examination is carried out to identify the development of complications. First, a specialist examines the patient and finds out when the first symptoms of the pathology were discovered.
Examination methods:
- Donate blood on an empty stomach. Glucose concentration is determined without the influence of food.
- Determine the amount of sugar after eating or taking glucose-containing medications.
- The dynamics of increasing and decreasing sugar during the day are monitored. Necessary to determine the correctness of the prescribed treatment.
- Delivery of urine to determine its composition (sugar, protein, acetone). In addition to causing renal dysfunction.
- A detailed blood test to determine the presence of a malfunction in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Further hardware examinations:
- Ultrasound;
- ECG;
- dopplerography;
- capillaroscopy.

A comprehensive examination allows you to determine the severity of the disease and its impact on organ function. If abnormalities are detected, the patient will be treated by different specialists, depending on which organs have been damaged.
Diagnostics is also necessary for people at risk of developing the disease (heredity, overweight, age over 45 years).
Treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Pathological therapy consists of complex treatment. Depending on the severity of the disease, the specialist prescribes medications, draws up a menu and prescribes physical exercises to lose weight.
Antihyperglycemic drugs
Type 2 diabetes is initially treated with diet.When the treatment does not produce a visible effect, the specialist prescribes drugs that lower the amount of sugar in the blood. At the beginning of treatment, 1 type of drug is prescribed. To ensure the effectiveness of treatment, the number of drugs is gradually increased.
Types of hypoglycemic drugs and their effects:
| Type of drugs | Their purpose |
|---|---|
| Glinides and sulfonylurea derivatives | Prescribed to increase the body's production of insulin. |
| Biguanides and glitazones | It reduces glucose production in the liver and increases tissue sensitivity to sugar. Helps reduce appetite. |
| Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors | Reduce the rate of glucose absorption by intestinal tissues. |
| Gliptins and glucagon-like peptide receptor agonists | They increase insulin production and at the same time reduce sugar concentration. |
| Insulin | Promotes the absorption of glucose by body tissues. |
| Thiazolidone derivatives | Increases the sensitivity of cellular receptors to insulin. |
Very often 2 or 3 mutually compatible drugs are prescribed. The simultaneous use of drugs to increase insulin production with drugs that affect the sensitivity of cells to the hormone will allow to achieve an effective reduction in blood sugar.
It is dangerous to choose drugs yourself. A sharp decrease in sugar concentration also has a detrimental effect on the functioning of the body. If the drug causes side effects, it is replaced by a therapist. If the drugs are ineffective, the patient is transferred to insulin therapy.
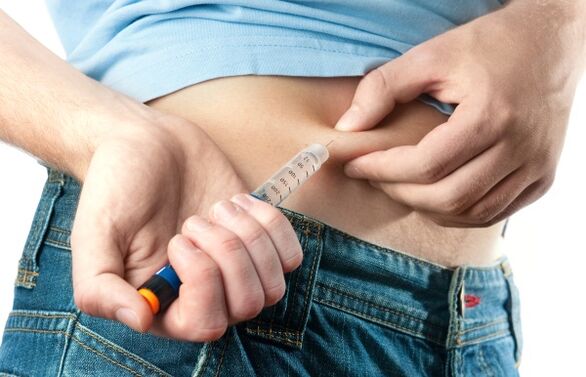
Insulin therapy
Insulin is prescribed as therapy when there is a decrease in the production of the hormone by the pancreas. The dose and number of injections depend on the type of diet prescribed and the degree of physical activity. An overweight patient with diabetes is prescribed a low-carbohydrate diet, which requires more frequent monitoring of glucose concentrations.
The use of injections allows you to maintain the functionality of the pancreas (the organ does not wear out due to increased load). It also reduces the chance of developing complications.
In addition, the use of injections allows:
- normalize the amount of sugar in the blood during the day;
- enhance the production of the hormone by the gland independently, in response to an increase in glucose concentration after eating food;
- reduce the formation of glucose from non-carbohydrate compounds;
- control glucose production in the liver;
- normalize the production of lipids and glucagon.
The injections are painless and are administered using a special syringe with markings to control the amount of the drug. Sugar levels are measured before and after the procedure.
Diet for type 2 diabetes. Nutrition principles
When treating diabetes, it is necessary to constantly follow a diet that depends on the severity of the disease, the presence of excess weight and physical activity. The menu must be agreed with the treating specialist. If the amount of sugar changes (increase or decrease), the therapist changes the diet.
When following a diet, important conditions must be observed:
- eating should happen at certain times at least 6 times a day;
- food should not be high in calories and easily digestible;
- if you are overweight, you need to reduce the calorie content of your meals;
- the amount of salt consumed should be reduced to a minimum;
- alcohol and fast food snacks are excluded;
- high fruit content and taking vitamin supplements to maintain immunity.
It is advisable to prepare dishes without using oil or with a minimum amount of it (you can boil or bake). It is necessary to increase the amount of clean water consumed every day. When creating a menu, be sure to take into account the presence of other pathologies (diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, heart, kidneys).
Prohibited products
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (diet and treatment will give a positive result with proper nutrition) in a mild form can be eliminated by eliminating harmful dishes and foods from the diet.
| Products strictly prohibited | Conditionally prohibited products |
|---|---|
|
|
The amount of consumption of conditionally prohibited products must be agreed with the treating specialist. They increase the amount of glucose, but gradually. It is prohibited to consume 2 or more types of products from the conditionally prohibited list at the same time.
How to monitor blood glucose levels if you have diabetes?
Diabetes requires regular monitoring of sugar levels.To measure it at home, a glucometer is used.It is mandatory to take daily morning measurements before eating. If possible, measure during the day (after eating, during strenuous physical activity).
All data must be entered in a special notebook, which must be shown to the therapist during the next visit. Therapy (medicines, diet) will be adapted based on the dynamics of glucose changes. Additionally, you need to undergo a laboratory test every 3-6 months (set by your doctor).
List of permitted products indicating GI
If you suffer from diabetes, you can consume the following foods in any quantity, but taking into account their calorie content and GI.
| Shopping list | GI (glycemic index) |
|---|---|
| Hard-boiled eggs | 48 |
| Boiled mushrooms | 15 |
| Sea cabbage | 22 |
| Boiled shrimp | 5 |
| Kefir | 35 |
| Soya milk | thirty |
| Cottage cheese | 45 |
| Tofu cheese | 15 |
| Low-fat milk | thirty |
| Broccoli | 10 |
| cucumbers | 10 |
| Tomato | 20 |
| Eggplant | 20 |
| Olives | 15 |
| Radish | 10 |
| Apples | thirty |
| Pear | 34 |
| Prune | 22 |
| Cherry | 22 |
| Rye flour bread | 45 |
| Dill | 15 |
| Salad | 10 |
| Pearl barley porridge on the water | 22 |
| Wholemeal pasta | 38 |
| Cereals | 40 |
| Bread | 45 |
| Jam | thirty |
This list can be expanded by the therapist, taking into account physical activity and the severity of the disease.
Folk remedies
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (diet and treatment are necessary conditions to prevent the development of complications and further development of the disease) can also be controlled with folk remedies. It is advisable to discuss their use with your doctor.
Recipes that normalize the metabolic process in the body and promote weight loss:
- Mix 70 ml of honey and 40 g of dry cinnamon (powdered) in 0. 4 liters of boiling water. Leave overnight in the cold. The drink is divided into 2 servings. Use morning and evening. The duration of therapy is up to 14 days.
- Steam 10-12 pieces in 0. 5 liters of water. Bay leaves. Use 30 ml 3 times. 10 day course. It is necessary to conduct 3 courses with 10-day breaks.
- Instead of tea leaves, steam lime blossoms. Drink up to 2 cups of tea a day.
- Finely chop 350 g of garlic and parsley and 100 g of lemon zest. Mix and leave to rest in the cold for up to 14 days. Take 10-12 mg daily.
- Boil 20 g of beans in 1 liter of water (4 hours). Consume up to 300 ml per day (divisible into portions). The duration of therapy is 31 days.
- Drinks prepared instead of tea (consume 400 ml per day) from:
- aromatic herbs St. John's wort, chamomile, blueberry;
- aspen bark;
- bean wings;
- whole cinnamon.

If there is an intolerance or allergic reaction, drinks are excluded from the diet.
Physical exercise
Physical warm-up should be performed even if there are no weight problems. Exercises allow you to normalize the functioning of the heart, blood vessels and respiratory organs, as well as stabilize the general condition of the body as a whole.
During physical activity, it is important to correctly take into account the load, since increased calorie consumption quickly leads to hunger, and food after exercise can be digested with a large release of glucose into the blood.
Recommended sports for diabetes:
- exercises with dumbbells;
- walks in the park or light jogging;
- riding a bicycle;
- I swim;
- yoga;
- dance calmly.

It is advisable to discuss the type of lesson with the treating specialist. As well as dedicating the necessary time to the procedure.
Complications of the disease
When the disease is detected in an advanced stage, inadequate treatment has been provided orthe patient did not follow the recommendations of the specialist, dangerous complications may develop:
- Swelling.Edema can develop not only outside (arms, legs, face), but also inside the body. Depending on what caused the symptom to develop. This could be the development of heart or kidney failure, which also develops as a complication of diabetes.
- Leg pain.The symptom is initially present during intense physical activity. As the disease progresses, the pain also occurs at night. Numbness of the limbs and temporary loss of sensation also appear. There may be a burning sensation.
- The appearance of ulcers.Due to the increased sugar content, wounds heal poorly and take a long time, which leads to the development of open ulcers. The therapist recommends treating even small cuts with care until the wound is completely healed.
- Development of gangrene. In diabetes, the condition of the blood vessels is disrupted, which can lead to their blockage. Most often this phenomenon is observed at the extremities. Due to the formation of a blood clot, fresh blood with oxygen and nutrients does not flow into the hand/foot. Tissue death occurs. Initially, redness occurs, accompanied by pain and swelling. If no treatment is done, it will eventually turn blue. The limb is amputated.
- Increase/decrease in pressure.Changes in blood pressure levels often occur due to kidney dysfunction.
- Coma.This condition can occur with a sharp increase or decrease in glucose concentration (due to an overdose of insulin). Or due to severe poisoning of the body with toxins produced during the formation of energy by fat cells. At the same time, the patient becomes covered with cold, sticky sweat, speech becomes slurred and unconscious. When glucose increases, the characteristic odor of acetone appears. Subsequently, loss of consciousness occurs. Without assistance, a quick death is possible.
- Visual impairment. Due to poor nutrition of the eye tissues and nerves. Spots and a veil appear initially, and complete blindness may gradually develop.
- Impaired renal function.Due to the heavy load on the organ, renal failure develops.
By treating diabetes, it is possible to avoid the development of consequences. Timely detection of the onset of complications will eliminate their further progression.
Clinical guidelines for type 2 diabetes
If diabetes is detected, an urgent visit to a doctor and a sugar test is required. If the disease is confirmed, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination. Next, you need to follow all the recommendations of the treating specialist (diet, medications, exercises). Be sure to check your blood sugar levels. If the condition changes, the treating doctor must adapt the treatment.
Diabetes mellitus can develop gradually and be detected already in the middle stage. In type 2, the basis of treatment is diet. In advanced cases, medications or insulin injections are required.